Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Hisano, Naoki*; Abe, Jun*; Suzuki, Akio*
American Mineralogist, 107(3), p.325 - 335, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.65(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The basaltic glass structure were investigated to 18 GPa using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction. The O-O coordination number (CN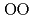 ) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r
) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r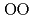 ) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN
) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN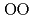 stops increasing and r
stops increasing and r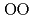 begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN
begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN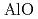 ) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN
) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN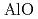 increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN
increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN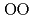 increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at
increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at  2 GPa.
2 GPa.
J. A. BERRY*; M. BROWNSWORD*; D. J. ILETT*; Linklater, C. M.*; Mason, C.*; TWEED, C. J.*
JNC TJ8400 2000-060, 60 Pages, 2000/02
Batch sorption experiments have been carried out to investigate the sorption behaviour of plutonium onto basalt and sandstone from the appropriate rock-equilibrated waters under different redox eonditions. Redox Potentials in solution were controlled by the addition of two reducing agents and one oxidising agent. Thermodynamic chemical modelling was undertaken to interpret the results. The sorption models were based on iron oxide. They adequately reproduced the data for sorption of plutonium onto sandstone, but tended to underpredict sorption onto basalt.
Ashida, Takashi; ; Sato, Haruo; ; Kitamura, Akira; Kawamura, Kazuhiro
JNC TN8400 99-083, 63 Pages, 1999/11
Studies on the chemical and migration behaviour of radionuclides were carried out in the Quantitative Assessment Radionuclide Migration Experimental Facility (QUALITY)for assuring the relaiability and for improving the propriety of data concerning nuclide migration used in the Second Progress Report for the geoloical disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Five studies for solubility, sorption and diffusion concerning nuclide migration were carried out. The overview of each study and the result is as follows: (1)Study on Effect of Carbonate on Np Solubility. Solubilities of Np(IV) were measured as functions of pH and carbonate concentration under reducing conditions. The obtained data could be well described by considering two hydroxo-carbonate complexes, and those stability constants were estimated and compared with the literature data. Consequently, the data obtained in this study were similar to the literature data. (2)Study on Effect of Carbonate on Np Sorption on Bentonite. Distribution coefficients (Kd) of Np(IV) on smectite were measured as a function of carbonate concentration. The obtained Kd values were approximately constant over the carbonate concentration (total carbon concentration 0.04-0.15M). The results of desorption tests by 1M KCl and HCl at the end of sorption experiments showed two different desorption behaviour; Np(IV) was well removed by HCl for the experiments in low carbonate concentration and by KCl for those in high carbonate concentration. (3)Distribution Coefficient Measurements for Cs, Pb and Cm on Rocks. Distribution Coefficients for Cs, Pb and Cm on Japanese major rocks (basalt, mudstone, sandstone, granodiorite and tuff) were measured as a function of ionic strength. The obtained Kd values were either the same orders or higher compared with data used to both fresh and saline groundwater systems in the Second Progress Report. This indicates that the Kd data used in the Second Progress Report are either proper or conservative. ...
G M N BASTON*; J A BERRY*; M BROWNSWORD*; D J LLETT*; C M LINKLATER*; S W SWANTON*; Tweed, C. J.*
JNC TJ8400 99-078, 72 Pages, 1999/03
A desk study has been carried out to establish the feasibility of measuring the oxidation state of plutonium under near-neutral strongly-reducing conditions. X-ray absorbance spectroscopy appears to be capable of establishing the oxidation state of plutonium sorbed on a suitable substrate. An experimental and modelling investigation has been performed to study the sorption of plutonium onto basalt, mudstone and sandstone under strongly-reducing conditions at three concentrations of carbonate. Appropriate synthetic rock-equilibrated de-ionised water and seawater were used. A model has been developed to describe the sorption of plutonium onto basalt, mudstone and sandstone in de-ionised water and seawater. Predicted R values are generally in good agreement with the observed experimental measurements. The model is based on sorption of plutonium(III) species and assumes iron oxide is the dominant sorbing phase.
values are generally in good agreement with the observed experimental measurements. The model is based on sorption of plutonium(III) species and assumes iron oxide is the dominant sorbing phase.
Sato, Haruo
PNC TN8410 97-202, 205 Pages, 1998/01
This thesis summarizes the results investigated in order to establish a basic theory on the predictive method of diffusion coefficients of nuclides in compacted sodium bentonite which is a candidate buffer material and in representative rocks for the geological disposal of radioactive waste by measuring the pore structural factors of the compacted bentonite and rocks such as porosity and tortuosity, measuring diffusion coefficients of nuclides in the bentonite and rocks, acquiring basic data on diffusion and developing diffusion models which can quantitatively predict nuclide migration in long-term. This consists of 7 chapters. Chapter 1 is the introduction, in which conventional studies on nuclide migration in buffer materials and rocks for the geological disposal of radioactive waste carried out to date are reviewed, and those problems are summarized as well as the objectives of this study are described. Besides, the difinition of geological disposal is explained. In Chapter 2, it is described on non-steady state diffusion of HTO, Sr-90, Tc-99, I-129, Cs-137, Np-237, Am-241 and Pu in purified sodium bentonite, Kunipia-F, in which the rate of constituent Na-smectite was raised approximately 100wt%. In-diffusion experiments were carried out in a range of bentonite densities of 200  2000 kg
2000 kg m
m under ambient aerobic conditions at room temperature (20
under ambient aerobic conditions at room temperature (20  23
23 C), and apparent diffusion coefficients (Da) were obtained. The apparent diffusion coefficients decreased with increasing dry density of bentonite. It was quantitatively indicated from diffusion experiments using HTO that these Da values include the effect of geometric retardation such as the tortuosity factor of compacted bentonite. It was experimentally clarified that Da is not affected by diffusion time based on diffusion experiments for different experimental periods using Sr and Cs. Moreover, it was also experimentally clarified that Da is not affected by tracer ...
C), and apparent diffusion coefficients (Da) were obtained. The apparent diffusion coefficients decreased with increasing dry density of bentonite. It was quantitatively indicated from diffusion experiments using HTO that these Da values include the effect of geometric retardation such as the tortuosity factor of compacted bentonite. It was experimentally clarified that Da is not affected by diffusion time based on diffusion experiments for different experimental periods using Sr and Cs. Moreover, it was also experimentally clarified that Da is not affected by tracer ...
; *; Tamura, Yukito; ;
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.353, 0, p.71 - 78, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Shibutani, Tomoki; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Sato, Haruo; Yui, Mikazu; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Ishiguro, Katsuhiko
PNC TN8410 92-163, 51 Pages, 1992/09
None
Yusa, Yasuhisa; ; Arai, Takashi
PNC TN8410 91-007, 18 Pages, 1990/12
This paper contains an overview of analogue studies for the assessment of long-term durability of engineered barrier materials at PNC Tokai. Materials of young age and with simple history are the most suitable for study as: (1)properties of the materials tend to deteriorate over longer historical time intervals; and (2) detailed quantitative data on time intervals and environmental conditions are more likely to be available. The following materials and their alteration phenomena were selected: (1)weathering alteration of basaltic glass (as vitrified waste form), (2)corrosion of iron in soil (as overpack), (3)illitization of smectite associated with contact metamorphism (as buffer material), (4)alteration of cement (as buffer or backfill material). (1)Weathering alteration of basaltic glass: Basaltic g1asses, from the Fuji and the Izu-Ohshima pyroclastic fall deposits were studied. The observations were made: (a)Climatological conditions have not varied significantly during the last three thousand years. Therefore, values for temperature, amount, and chemistry of ground water are quantified. (b)The cases studied could be regarded as leaching experiments in groundwater, using mass balances in water-g1ass interaction. (c)Although the groundwater is of Ca(Mg)-HCO type in the Fuji area and of Na-Cl type in the Izu-Ohshima, similar alteration ratios (2
type in the Fuji area and of Na-Cl type in the Izu-Ohshima, similar alteration ratios (2 3
3 m/1000yr) were obtained. (2)Corrosion of iron in soil: Industrial materials, such as gas/water service pipes of carbon steel or cast iron embedded in soil for 20
m/1000yr) were obtained. (2)Corrosion of iron in soil: Industrial materials, such as gas/water service pipes of carbon steel or cast iron embedded in soil for 20  110 years, were selected for an analogue study of corrosion of iron in bentonite. The maximum corrosion rates obtained so far fall in the range of 0.04
110 years, were selected for an analogue study of corrosion of iron in bentonite. The maximum corrosion rates obtained so far fall in the range of 0.04 0.09 mm/yr. (3)Illitization of smectite associated with contact metamorphism: In the Murakami bentonite deposit in central Japan, lateral variation of smectite to smectite/illite mixed-layer minerals are found in the aureole of the rhyolite intrusion body. Conversion of smectite to the
0.09 mm/yr. (3)Illitization of smectite associated with contact metamorphism: In the Murakami bentonite deposit in central Japan, lateral variation of smectite to smectite/illite mixed-layer minerals are found in the aureole of the rhyolite intrusion body. Conversion of smectite to the
M.J.Jercinovic*; Murakami, Takashi; R.C.Fwing*
Water-Rock Interaction, p.337 - 340, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
 C 300MPa
C 300MPa; ;
JAERI-M 85-014, 16 Pages, 1985/02
no abstracts in English
; *; *; ; Araki, Kunio;
JAERI-M 9247, 28 Pages, 1980/12
no abstracts in English